Transgenic Plants Animals Definition

GMO An organism whose genetic characteristics have been altered by the insertion of a modified gene or a gene from another organism using the.
Transgenic plants animals definition. Transgenic Plants as Bioreactor Molecular Farming. There are two techniques for introducing foreign genes transgenes into the plant cell genome. Plant cells act as the Natures cheapest factory.
Transgenic animal genetically engineered animalor offspring of genetically engineeredanimals. Transgenic animals are those that have been genetically modified. Sheep goats pigs cows rabbits rats mice fish insects parasites and even humans have previously been used in this modification process.
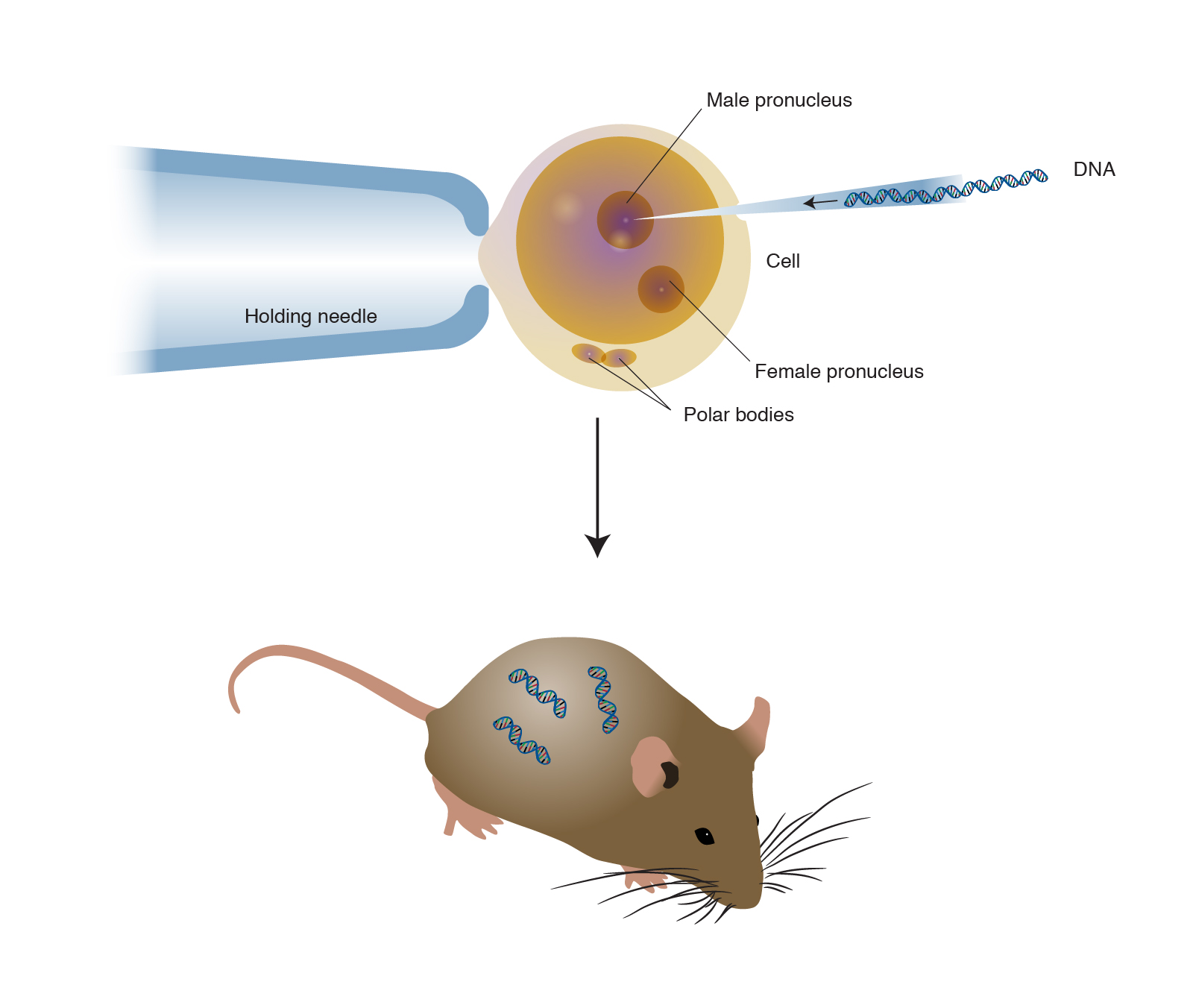
Transgenic plants and animals Transgenic plants are plants that have been genetically engineered a breeding approach that uses recombinant DNA techniques to create plants with new characteristics. Animals usually are made transgenic by having a small sequence of foreign DNA injected into a fertilized egg or developing embryo. Transgenesis is the phenomenon in which a foreign gene with desired characteristics is introduced into the genome of the target animal.
These genes are passed on to the successive generations. The foreign gene that is introduced is known as the transgene and the animal whose genome is altered is known as transgenic. A transgenic animal is one whose genome has been altered by the transfer of a gene or genes from another species or breed.
Transgenic animal synonyms Transgenic animal pronunciation Transgenic animal translation English dictionary definition of Transgenic animal. Plants and animals become genetically modified in nature too. Genetically enginnered animal or offspring of genetically engineered animals.
In addition to the gene itself the DNA usually includes other sequences to enable it to be incorporated into the DNA of the host and to be expressed correctly by the cells of the host. Transgenic models are more precise in comparison to traditional animal models for example the oncomouse with its increased susceptibility to tumor development enables results for carcinogenicity studies to be obtained within a shorter time-frame thus reducing the course of tumor development in experimentally affected animals. The transgenic animal usually contains material from at lease one unrelated organism such as from a virus plant or other animal.